I tried to go a website. It was giving message popup blocking is blocking the website. So,
- I allowed popup for that website.
- I changed in the registry settings to allow the website
- I added the website in trusted zone it did not work
- I allowed the website in the smoothwall it did not work
I've managed to get around the IE9 and Pop-up blocker issue as follows:
Scenario: Running 2008 R2 SP1, with Windows 7 SP1 + IE9 clients. Setting Pop-up exceptions on this GPO (even with the KB2530309 fix) does not work:
User Config > Policies > Admin Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer - Pop-up allow list - Enabled
To get around this problem, install KB2530309, then navigate to:
User Config > Preferences > Control Panel Settings - Internet Settings
Right click Internet Settings > New > Internet Explorer 8 (Note: With the KB2530309 fix, this applies to both IE8 and IE9).
Select the Privacy tab > Settings. Enter your Pop-up exceptions here and apply changes.
Now run gpupdate /force on your workstation or restart your workstation. Pop-up exceptions will now work correctly with IE9.
==============Not possible without domain admin privilege
Then I followed this:
- Open the IE9
- Tools-->Internet Option-->Advanced tab-->Click the Reset button to Reset the Internet Explorer settings
- Restarted my computer and it worked
=====================================================
Personally, I use the following policy:
Computer Configuration - Admin Templates - Windows Components/Internet Explorer/Internet Control Panel/Security Page/Internet Zone --- "Use Pop-up Blocker" ENABLED, with the option set to Disable.
Adding Pop-up blocker exception via group policy:
Personally, I use the following policy:
Computer Configuration - Admin Templates - Windows Components/Internet Explorer/Internet Control Panel/Security Page/Internet Zone --- "Use Pop-up Blocker" ENABLED, with the option set to Disable.
Adding Pop-up blocker exception via group policy:
1) Navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer
2) Double click on ‘Pop-Up Allow List’
3) Enable
4) Add URL
5) Apply changes
How to add trusted sites to group policy?
See Computer Configuration --- Administrative Tools --- Windows Components --- Internet Explorer --- Internet Control Panel --- Security Page and then double click to the "Site to zone assignment list".
Enable it, click Show, add website as value name and 1, 2, 3 or 4 as value.
1. Intranet zone
2. Trusted Sites zone
3. Internet zone
4. Restricted Sites zone
2. Trusted Sites zone
3. Internet zone
4. Restricted Sites zone
Tools-->Internet option GPO in Windows Server 2008 should be:
User Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Internet Explorer\Browser menus. Enable the Group Policy “Tools menu: Disable Internet Options… menu option”
Reset all zones to default level using GPO:
1. Close the Internet Explorer on the client machine.
2. User Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Internet Explorer Maintenance -> Security
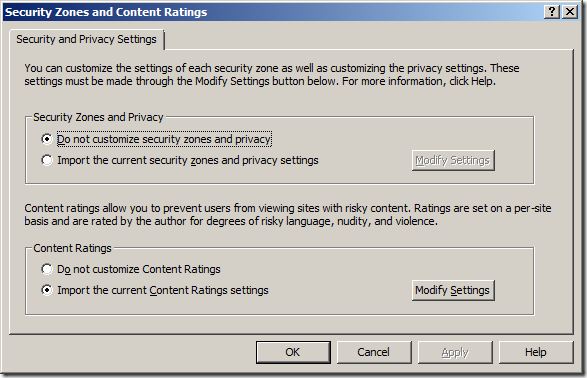
3. Double click Security Zones and Content Ratings.
4. Select Import the current security zones and privacy settings check box, click Modify Settings.
5. At the Security Tab, click Reset all zones to default level.
6. Run gpupdate /force to applied the policy successfully.
Reset Internet Explorer settings(any policy settings that are specified to that Group Policy are reset):
======================
1. User Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Internet Explorer Maintenance
2. Right-click Internet Explorer Maintenance, and then click Preference Mode.
If a policy is already defined, you must click Reset Browser Settings before you can place this policy in Preference mode. When you reset the browser settings, any policy settings that are specified to that Group Policy are reset.
======================
1. User Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Internet Explorer Maintenance
2. Right-click Internet Explorer Maintenance, and then click Preference Mode.
If a policy is already defined, you must click Reset Browser Settings before you can place this policy in Preference mode. When you reset the browser settings, any policy settings that are specified to that Group Policy are reset.
I stumbled on the same phenomenon.
Apparently, on server2008, despite a domain-wide GPO was applied dictating the trusted sites zone, it seemed to be NOT applied to server2008 !
More specifically, you can see in Internet Options, tab Security, a yellow info line stating that "Some settings are managed by your system administrator", but when checking the list with Trusted sites, this turns out to be empty !
Apparently, on server2008, despite a domain-wide GPO was applied dictating the trusted sites zone, it seemed to be NOT applied to server2008 !
More specifically, you can see in Internet Options, tab Security, a yellow info line stating that "Some settings are managed by your system administrator", but when checking the list with Trusted sites, this turns out to be empty !
The exact GPO setting I'm referring to:
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel > Security Page :
Site to Zone Assignment List ENABLED
With (example):
http://*.myowncompany.com 2
http://*.microsoft.com 2
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel > Security Page :
Site to Zone Assignment List ENABLED
With (example):
http://*.myowncompany.com 2
http://*.microsoft.com 2
Despite this setting, when checking in IE on any Server2008, the list of sites in Trusted Zone is EMPTY !!
This is caused by the fact that by default Internet Explorer Enhanced Security Configuration (IE ESC)is ENABLED for both users and administrators !
You can disable it for administrators:
Start > Administrative Tools > Server Manager
under Security Information, click Configure IE ESC
Start > Administrative Tools > Server Manager
under Security Information, click Configure IE ESC
Under Administrators : click Off.
Now, after closing and reopening IE, you will find the list with Trusted Sites in place !
Now, after closing and reopening IE, you will find the list with Trusted Sites in place !
How to configure Internet Explorer to Allow and Block URL’s
Step 1. Edit a Group Policy Object (GPO) that applies to the users you want to configure URL blocking.
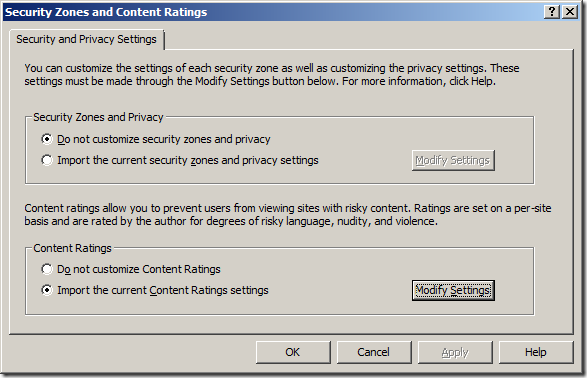
Step 2. Navigate to User Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Internet Explorer Maintenance > Security and then click on the “Security Zones and Content Ratings”
Step 3. Select “Import the current Content Ratings settings” and then click on the “Modify Settings” button
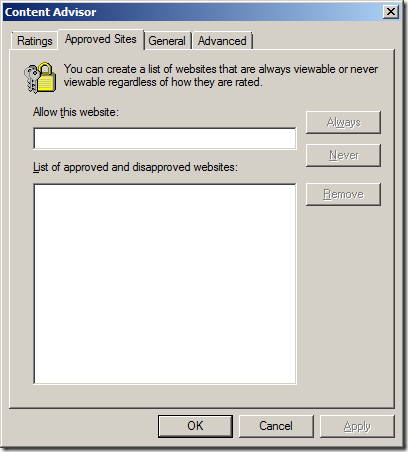
Step 4. Click on the “Approved Sites” tab
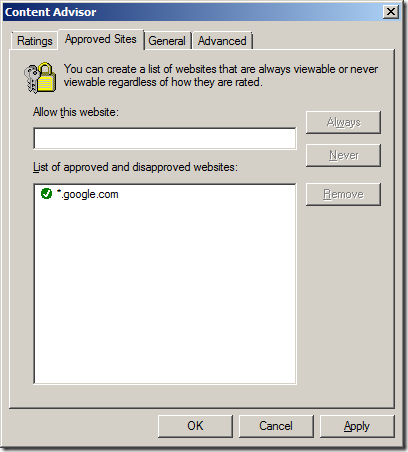
Step 5a (Black List). Type the name of the URL that you want to block in the “Allow this website” text field and then click “Never” then “OK”
Step 5b (White List). However if you are trying to maintain a white list of URL’s then type the name of the site you want to allow it the “Allow this website” text field and then click “Always” then “OK”
Note: You will probably want to add the internal domain name of your companies AD to the Allow list of as well to ensure users can access the intranet web sites. Also note that while wildcards are supported in the URL’s, but adding just the URL “*” does not work. While this would be very handy to configure a white list I will show you how to get around this restriction in further steps below.
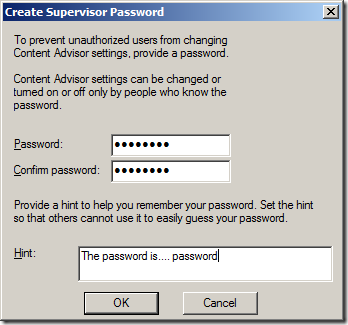
Now we have to create a supervisor password that will be used for making any subsequent changes to the Allow/Never URL list. This password can also be used by the user (if they know it) to work around these URL restrictions. However as this password is applied by policy it will be the same password for all users so think about chancing the password often.
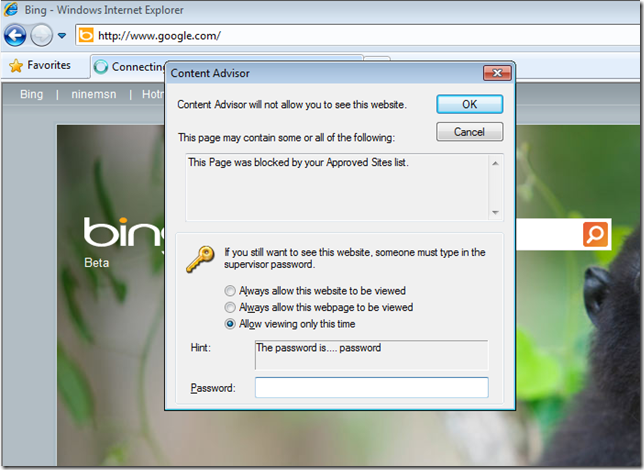
Step 6. Type the same password in both the “Password” and “Confirm Password” fields and type at hint in the “hint” field. You could also type something like “To get this password please contact the help desk on 5555-5555”.
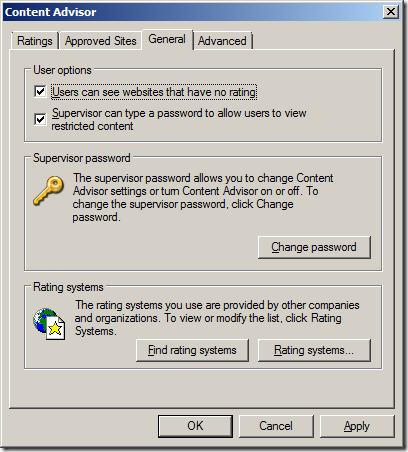
By default when you enable the content advisor it will automatically block any web site that does not have a rating configured. Therefore you will want to turn this blanket restriction off in step 8 if you all you are trying to do is block specific URL’s in a black list configuration.
Step 8 (Black List). Tick “User can see websites that have no rating” then click “OK”
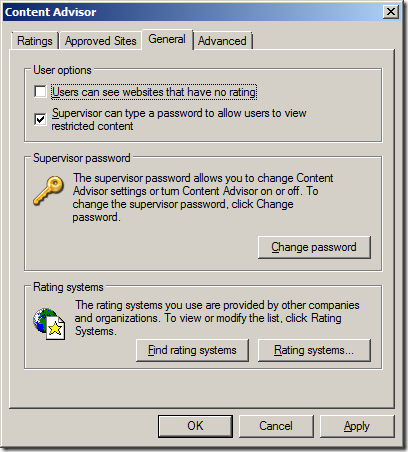
Note: For white list configuration leave the “User can see websites that have no rating” un-ticked so that all web sites will be blocked.
Step 9. Click OK
Done.
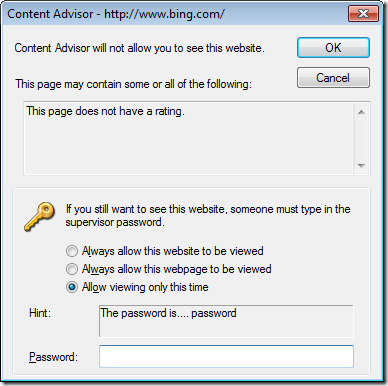
If you configured a black list then a user will be allowed to go to all web sites except the URL that you specifically blocked. When the user does hit a web site that is blocked they will be presented with dialogue box explaining why they are not able to visit the web site and an option to visit the site only if they know the supervisor password.
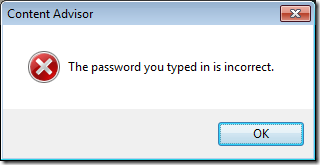
If they click Cancel nothing will happen and if they press OK they will get presented with this dialogue box.
Below is another example message that is presented when visiting a site without a rating and you have configured the policy not load sites that do not have a rating which you will see if you have configured this as a white list.
If you are using a white list configured and a users will still be able to visiting as site so long as it is ICRA3 rated and it does not report as having content that falls into any of the rating categories. Therefore this method is not 100% affective for a white list strategy but you do find your users visiting a site that is not specifically allowed then you can simply added it as a blocked URL.
 I have previously talked about the new Group Policy for IE9 ,however I mention that one of the issues was that there is currently no “official” support of Group Policy Preferences… Unfortunately there is still no “official” support but it is now possible if you do some really easy XML editing…
I have previously talked about the new Group Policy for IE9 ,however I mention that one of the issues was that there is currently no “official” support of Group Policy Preferences… Unfortunately there is still no “official” support but it is now possible if you do some really easy XML editing…
How to enable Group Policy Preferences support for IE9
 I have previously talked about the new Group Policy for IE9 ,however I mention that one of the issues was that there is currently no “official” support of Group Policy Preferences… Unfortunately there is still no “official” support but it is now possible if you do some really easy XML editing…
I have previously talked about the new Group Policy for IE9 ,however I mention that one of the issues was that there is currently no “official” support of Group Policy Preferences… Unfortunately there is still no “official” support but it is now possible if you do some really easy XML editing…
Mark Heitbrink (fellow Group Policy MVP) has published an article which explains why it does not work and explains briefly how to modify the XML file for Group Policy Preferences so it will apply setting to IE9.
Therefore taking Mark excellent information I have gone thought the process step by step below showing what I think is the easiest way to find and edit the XML file to enable GPP for IE9.
Step by Step enabling GPP for IE9
Step 1. Setup a IE8 Internet Explorer Extension setting that has the setting you want to apply to IE9. (e.g. Home Page)
Step 2. In the same Group Policy Object navigate to User Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Scripts (Logon/Logoff) and double click on the Logon (or logoff) option. Then click on the “Show Files” button.
Step 3. Click on “Users” in the Address bar.
Step 4. Then click on the “Preferences” and then “InternetSettings” folder and then right click on the “InternetSettings” file and click on “Edit”.
Now we are looking at the XML that is used to apply the Group Policy Preferences settings. This is where we need to change the version number to support IE9.
Tip: Enable “Word Wrap” in notepad to see the text on multiple lines.
Step 5. Change “max=9.0.0.0” to “9.1.0.0” (see below)
Before:
Before:
After:
Step 6. Save the file and you are done.
Now you can have the goodness of Group Policy Preferences with IE9, however as the article also said this is NOT supported so please test carefully.
What is also nice about this change is that it will be persistence, so if you make subsequent changes to the same setting you do not need to edit the XML again however you will need to make this change each time you make a new GPP IE Policy setting.
Source: Internet Explorer 9(IE9) Group Policy Preferences (GPP) (Via GPOGuy )

![image[83] image[83]](http://www.grouppolicy.biz/wp-content/uploads/2010/07/image83_thumb.png)







.png)